A document's color scheme addresses its use of color, which can be a important way to establish consistency and meaningful contrast. There are two fundamental color models in document design: CMYK—which stands for Cyan (blue), Magenta (red), Yellow, and Key (usually black)—is a subtractive color model used when designing for print; RGB—which stands for Red, Green, and Blue—is an additive color model used when designing for the screen. Color schemes can be articulated with a color wheel: 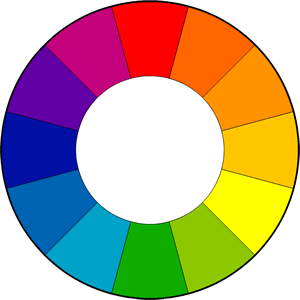
The wheel contains the three primary colors: blue, red, and yellow. If each is mixed with its neighbor the result is the secondary colors: green, orange, and purple. Repeating this process for the primary and secondary colors results in the intermediary tertiary colors. This completes the standard 12-color wheel, with which it is possible to identify different types of color relationships:
The warm half of the color wheel contains hues with red or yellow in them; the cool half contains hues with blue. Warm colors tend to be used for impactful accents; cool colors tend to recede into the background. This reference chart helpfully articulates different color scheme elements. |
Handbook >